In this test, I used an ESP32 development board, an ADS1115 16-bit analog-to-digital converter, and an SM-24 geophone sensor to capture seismic signals generated by human footfalls.
Rather than relying on an external analog bandpass filter, which often introduces additional electrical noise. I implemented a digital bandpass filter directly on the ESP32 microcontroller. This software-based signal conditioning approach enabled more precise control over frequency filtering and reduced hardware complexity. The filter was designed to pass frequencies in the 5 Hz to 60 Hz range, which corresponds to the dominant frequency band of human footfall vibrations.
The complete sensor setup for footfall vibration acquisition is illustrated below:
Based on insights from prior research studies, the SM-24 geophone sensor exhibits higher accuracy and signal stability when buried at a depth of approximately 20 centimeters. To maximize seismic wave sensitivity, the sensor in this experiment was embedded 20 cm below the ground surface, ensuring optimal coupling with the earth for detecting footfall-induced vibrations.
The ESP32 microcontroller was connected to a computer via USB serial communication, functioning as the real-time interface for vibration data transmission. The ESP32 firmware was programmed to sample analog seismic signals from the SM-24 geophone using the ADS1115 16-bit ADC module at a sampling rate of 200 Hz. The digitized data was then streamed directly to the computer.
On the computer side, a Python-based data logger was employed to record incoming vibration signals and analyze seismic waveforms in the time domain. Special attention was given to identifying patterns and periodicity associated with human footfall activity, enabling classification based on signal peaks and their spacing.
The diagram below shows a time-domain seismic waveform recorded during a typical walking sequence. Each peak-trough cycle represents a vibration event generated by an individual footstep.
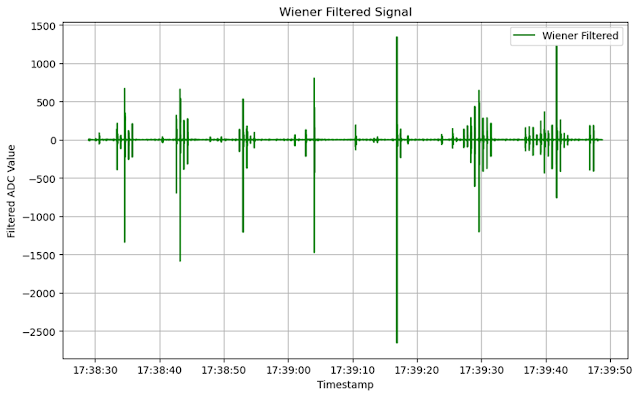
The raw seismic waveform captured by the geophone often contains background noise from environmental and electrical sources, which can mask the subtle patterns associated with human footfalls. To enhance the clarity of the signal and improve detection accuracy, I applied software-based noise reduction techniques. Several well-known digital filtering methods can be used for this purpose, including:
- Wiener filtering – ideal for stationary noise environments
- Median filtering – effective in removing spike-like anomalies
- Wavelet-based denoising – powerful for isolating transient signals like footfalls
By applying these advanced signal processing algorithms, the resulting waveform shows a significant reduction in noise. As illustrated below, the enhanced seismic waveform provides a much clearer and more distinguishable representation of footfall-induced vibrations, making it more suitable for further analysis and AI-driven classification.
By applying Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) and spectrogram analysis, we can effectively uncover the dominant frequency components embedded in seismic signals produced by human footfalls. These frequency-domain visualizations reveal subtle patterns and periodic structures that are often hidden in raw time-domain waveforms.
This deeper level of spectral analysis provides the foundation for building automated footstep detection systems. The extracted frequency features can be utilized as input for machine learning and AI models, enabling real-time classification of human activity based on vibration data captured from the ground.
In the upcoming chapter, I will explore advanced signal processing techniques and demonstrate how to develop AI-driven algorithms for real-time footfall detection and activity recognition using seismic data collected from geophone sensors and IoT-enabled microcontrollers.







Comments
Post a Comment